SCMS.pro Installation Guide
Introduction
SCMS.pro consists of Web Application and Cluster Frontend. Web Application handles user requests, transfers them to Cluster Frontend and gives back the result. Cluster Frontend, called Hydra, consists of scripts to interact with cluster software.
SCMS.pro is usually installed on two servers: web server and cluster frontend server. These could be real or virtual machines. It is also possible to combine both servers into a single one.
Web Application part is installed on web server. For security reasons Web Application should use https protocol.
Hydra is a tool for interaction between web application and cluster. It consists of two parts: Hydra client, which is installed to web server, and hydrad on cluster frontend.
Hydra configurator supports two installation modes: hctl for web server (client-only hctl) or for cluster frontend server (hydrad, perl libraries).
Hydra is installed on both servers: client part of hydra is on web server, and server part is on cluster frontend server.
There are two options for SCMS.pro to identify cluster users: using LDAP directory or PAM. LDAP is recommended.
All third-party software is configured according to it's documentation.
General requirements
- For Cluster Frontend server:
- C compiler (gcc)
- Perl 5.8+
- Perl libraries:
- Config::General
- Cwd
- Date::Parse
- DBD::mysql
- DBI
- Expect
- File::Basename
- File::Temp
- Getopt::Std
- IO::Stty
- JSON
- List::Util
- cron
- rsync
- For Web Application server:
- cron
- vim
- Apache 2.0, mod_ssl, mod_php
- PHP 5.3+, php-common, php-json, php-mbstring, php-mysql, php-session
- php-ldap (in case of LDAP)
- php-pam (in case of PAM)
- MySQL 5.x
- One of grid middlewares:
- ARC 0.8+
- gLite
- Unicore
The same timezone setting must be set for both servers, including system timezone, PHP and MySQL timezone settings. Both servers must syncronize time via NTP.
SCMS.pro Installation
It is often convenient to have virtual machines for different servers, each of which provides separate service and consumes rather small amount of resources. That’s why cluster frontend and web server can be virtual machines based on OpenVZ, KVM, Xen or other virtualization technology.
Installation SCMS.pro middleware on cluster frontend
Suppose you have computing cluster running and configured. Local job submission and job queues are managed by SLURM or Torque batch systems. User accounts are in OpenLDAP or just simply in /etc/passwd.
On cluster frontend user accounts and batch system should be configured properly. If users use grid, also grid middleware should be installed on cluster frontend.
Additionally, for Hydra should be installed perl, gcc, cron, rsync, and disabled SELinux. Installation example for CentOS 5 and 6:
Compile and install SCMS.pro Hydra hctl to /opt/hydra/bin.
tar zxf scms-pro-latest.tar.gz cd scms-pro/hydra
Change HANDSHAKE 1,2 private keys for communication between cluster frontend and web server in src/privatekey.h.
# Compile Hydra server: ./configure --prefix=/opt/hydra --enable-server --enable-client --enable-arc make make install
Here:
--prefix— installation prefix (directory);--enable-server— compile Hydra server;--enable-client— compile Hydra client;--enable-ng— enable ARC 0.x support (only for Hydra server);--enable-arc— enable ARC 1.x support (only for Hydra server).
Copy compiled Hydra client to web server.
Note, that hctl binary must be installed on Web server, and hydrad on Cluster Frontend server.
Set Hydra server parameters in /opt/hydra/etc.
In /opt/hydra/etc/modules.conf:
# Resource manager can be slurm, torque RESOURCE_MANAGER = slurm # Grid middleware GRID = grid_ng
GRID parameter options are:
- empty string — no grid support (default value)
grid_ng— ARC 0.8grid_arc— ARC 1.0grid_glite— gLitegrid_unicore— Unicore
In /opt/hydra/etc/mysql.conf:
MYSQL_SERVER = webserver_name MYSQL_USER = root MYSQL_PASSWD = mysql-pass MYSQL_DATABASE = scms-pro
Note: these MySQL config options should be used in future when creating MySQL database and user.
In /opt/hydra/etc/grid.conf:
# Path to grid commands GRID_PREFIX = /usr/bin # Path to globus commands, for example grid-proxy-init GLOBUS_PREFIX = /usr/bin # Additional Globus libraries for LD_LIBRARY_PATH if needed GLOBUS_LIBS =
For SLURM in /opt/hydra/etc/slurm.conf set:
# SLURM module config # SLURM commands path SLURM_PREFIX = "/opt/slurm/bin" # Local cluster name CLUSTER = my cluster # MPI SECTION SLURM_MPI_LAUNCHER = /opt/slurm/bin/run.ompi # Compilation Section # These options can be partition/queue dependent. # They are devided into blocks for each partition. C_FILEMASK = "*.c" C++_FILEMASK = "*.cpp" F77_FILEMASK = "*.f" F90_FILEMASK = "*.f90" # Cluster partitions and their config <PARTITION batch> PROCESSORS_PER_NODE = 8 GNU_C = /opt/ompi/1.2.4/gcc/4.1/bin/mpicc Intel_C = /opt/ompi/1.2.4/intel/10.1/bin/mpicc GNU_C++ = /opt/ompi/1.2.4/gcc/4.1/bin/mpic++ Intel_C++ = /opt/ompi/1.2.4/intel/10.1/bin/mpic++ GNU_F77 = /opt/ompi/1.2.4/gcc/4.1/bin/mpif77 GNU_F90 = /opt/ompi/1.2.4/gcc/4.1/bin/mpif90 Intel_F77 = /opt/ompi/1.2.4/intel/10.1/bin/mpif77 Intel_F90 = /opt/ompi/1.2.4/intel/10.1/bin/mpif90 C_LIBS = FORTRAN_LIBS = </PARTITION>
Run basic functional tests:
./scripts/verify.pl -p /path/to/hydra
Note: this script should be run under ordinary user.
Start Hydra server:
cp /opt/hydra/etc/init.d/hydrad /etc/init.d chkconfig hydrad --level 3 on service hydrad start
Set crontab task:
*/5 * * * * /opt/hydra/libexec/monitoring/grid_jobget-cron */10 * * * * /opt/hydra/libexec/monitoring/grid_clusters-cron
Installation SCMS.pro middleware on web server
Suppose that SCMS.pro is installed to http://example.com/. Disable SELinux. Install cron, apache, php 5.3+ and mysql.
If you use LDAP authentication, install php-ldap module.
If you use PAM for user authtentification, configure php-auth-pam module to work with PHP scripts:
yum install php-pear pecl search pam pecl install PAM
Add to /etc/php.ini:
extension = "pam.so" pam.servicename = "php"
Make /etc/shadow readable for Apache user group.
Configure Apache virtual host on web server. We strongly recommend disabling suexec_module, forbiding directory listing
(Option -Indexes in httpd.conf) and use ssl-enabled configuration.
Example of ssl-enabled configuration is given below. Server certificate can be generated using OpenSSL tools.
Listen 443 <VirtualHost *:443> SSLEngine On SSLCertificateFile conf/ssl/scms.crt SSLCertificateKeyFile conf/ssl/scms.key ServerName example.com DocumentRoot /var/www/example.com DirectoryIndex index.php RewriteEngine On <Directory "/var/www/example.com"> Options -Indexes FollowSymLinks AllowOverride All Order allow,deny Allow from all </Directory> TransferLog logs/example.com-access_log ErrorLog logs/example.com-error_log </VirtualHost>
Configure php module, in /etc/php.ini set:
; set your timezone setting date.timezone = Europe/Kiev safe_mode = Off short_open_tag = On display_errors = On register_globals = Off magic_quotes_gpc = Off memory_limit = 10M post_max_size = 10M ; maximum size of file you want to be uploaded through web application upload_max_filesize = 1000M default_socket_timeout = 60
memory_limit should be greater than post_max_size and post_max_size should be greater than upload_max_filesize.
Copy SCMS.pro files form webapp directory to /var/www/example.com. Change owner of /var/www/example.com to Apache.
Change /var/www/example.com/site/config.php file: set up MySQL login data and database name, authorization method (LDAP or PAM), LDAP details, path to Hydra.
Start Apache.
Run http://example.com/install/verify.php script in your browser. In case of errors you should fix them and run the script once again.
Run http://example.com/install.php script to populate MySQL database with tables and initial data.
Remove install directory. Test connection to SCMS.pro with your cluster login and password.
Sample SCMS.pro Installation
Below we give sample instructions on how to install and configure SCMS.pro. Before you proceed you should realize that these instructions are not to be followed blindly. They may not even work in your particular case. But we hope they should give you full understanding of how do you have to act on your cluster. Please feel free to contact us if you have any troubles while installation of SCMS.pro. We will appreciate if you share your experience to us.
Consider situation when you have two servers: web server called websrv and cluster frontend (cluster access) server called frontend, both running Linux CentOS 5 or 6. Cluster users are in LDAP Directory, resource manager is SLURM,
domain name for SCMS.pro is http://example.com/.
Download SCMS.pro archive from project site.
Install software on frontend server:
Disable SELinux in /etc/selinux/config:
SELINUX = disabled
and reboot server.
Set system timezone:
cp /usr/share/zoneinfo/Europe/Kiev /etc/localtime
Install the following packages if they are not exist. Packages perl-Expect, perl-IO-Stty exist in Epel and repoforge repositories. We may need add one of them to repository list.
yum -y install perl-Config-General.noarch yum -y install perl-TimeDate.noarch yum -y install perl-JSON.noarch yum -y install perl-LDAP.noarch yum -y install perl-DBD-MySQL yum -y install perl-Expect yum -y install rsync yum -y install gcc yum -y install cronie
Compile Hydra:
tar zxf scms-pro-latest.tar.gz cd scms/hydra # Change HANDSHAKE 1,2 private keys in src/privatekey.h # Compile Hydra server: ./configure --enable-server --enable-client --prefix=/opt/hydra --enable-arc make make install # Copy Hydra client to websrv: scp /opt/hydra/bin/hctl websrv:/opt/hydra/bin/ rm /opt/hydra/bin/hctl
Here we compiled and installed Hydra server to /opt/hydra/bin.
Set Hydra server parameters in /opt/hydra/etc.
In /opt/hydra/etc/modules.conf:
# Resource manager can be slurm, torque RESOURCE_MANAGER = slurm # Grid middleware GRID = grid_ng
GRID parameter options are:
- empty string — no grid support (default value)
grid_ng— ARC 0.8grid_arc— ARC 1.0grid_glite— gLitegrid_unicore— Unicore
In /opt/hydra/etc/mysql.conf:
MYSQL_SERVER = websrv MYSQL_USER = root MYSQL_PASSWD = mysql-pass MYSQL_DATABASE = scms-pro
Note: these MySQL config options should be used in future when creating MySQL database and user.
In /opt/hydra/etc/grid.conf:
# Path to grid commands GRID_PREFIX = /usr/bin # Path to globus commands, for example grid-proxy-init GLOBUS_PREFIX = /usr/bin # Additional Globus libraries for LD_LIBRARY_PATH if needed GLOBUS_LIBS =
For SLURM in /opt/hydra/etc/slurm.conf set:
# SLURM module config # SLURM commands path SLURM_PREFIX = "/opt/slurm/bin" # Local cluster name CLUSTER = my cluster # MPI SECTION SLURM_MPI_LAUNCHER = /opt/slurm/bin/run.ompi # Compilation Section # These options can be partition/queue dependent. # They are devided into blocks for each partition. C_FILEMASK = "*.c" C++_FILEMASK = "*.cpp" F77_FILEMASK = "*.f" F90_FILEMASK = "*.f90" # Cluster partitions and their config <PARTITION batch> PROCESSORS_PER_NODE = 8 GNU_C = /opt/ompi/1.2.4/gcc/4.1/bin/mpicc Intel_C = /opt/ompi/1.2.4/intel/10.1/bin/mpicc GNU_C++ = /opt/ompi/1.2.4/gcc/4.1/bin/mpic++ Intel_C++ = /opt/ompi/1.2.4/intel/10.1/bin/mpic++ GNU_F77 = /opt/ompi/1.2.4/gcc/4.1/bin/mpif77 GNU_F90 = /opt/ompi/1.2.4/gcc/4.1/bin/mpif90 Intel_F77 = /opt/ompi/1.2.4/intel/10.1/bin/mpif77 Intel_F90 = /opt/ompi/1.2.4/intel/10.1/bin/mpif90 C_LIBS = FORTRAN_LIBS = </PARTITION>
Run basic functional tests:
./scripts/verify.pl -p /opt/hydra | less
Start Hydra server:
cp /opt/hydra/etc/init.d/hydrad /etc/init.d chkconfig hydrad --level 3 on service hydrad start
Set crontab task:
*/5 * * * * /opt/hydra/libexec/monitoring/grid_jobget-cron */10 * * * * /opt/hydra/libexec/monitoring/grid_clusters-cron
Install software on websrv
Disable SELinux in /etc/selinux/config:
SELINUX=disabled
and reboot server.
Set system timezone:
cp /usr/share/zoneinfo/Europe/Kiev /etc/localtime
Install packages if they are not exist:
yum -y install vim # Apache and PHP yum -y install php yum -y install httpd yum -y install mod_ssl yum -y install mod_php # PHP modules yum -y install php-common yum -y install php-json yum -y install php-mbstring yum -y install php-session # PHP LDAP support yum -y install php-ldap # MySQL yum -y install mysql yum -y install mysql-server # Copy Web Application folder mkdir -p /var/www/example.com cp -r /tmp/scms-pro/webapp/* /var/www/example.com/ chown -R apache.apache /var/www/example.com # Set Hydra client permissions chgrp -R apache /opt/hydra/ chmod g+rx /opt/hydra/bin/hctl
Configure Apache, add to /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf:
Listen 443 <VirtualHost *:443> SSLEngine On SSLCertificateFile conf/ssl/scms.crt SSLCertificateKeyFile conf/ssl/scms.key ServerName example.com DocumentRoot /var/www/example.com DirectoryIndex index.php RewriteEngine On <Directory "/var/www/example.com"> Options -Indexes FollowSymLinks AllowOverride All Order allow,deny Allow from all </Directory> TransferLog logs/example.com-access_log ErrorLog logs/example.com-error_log </VirtualHost>
Configure PHP, change in /etc/php.ini:
date.timezone = Europe/Kiev safe_mode = Off short_open_tag = On display_errors = On register_globals = Off magic_quotes_gpc = Off post_max_size = 10M upload_max_filesize = 1000M default_socket_timeout = 60
To configure MySQL run commands:
service mysqld start /usr/bin/mysql_secure_installation > Set root password? [Y/n] Y > Remove anonymous users? [Y/n] Y > Disallow root login remotely? [Y/n] n > Remove test database and access to it? [Y/n] Y > Reload privilege tables now? [Y/n] Y mysql -u root -p # Create MySQL database mysql> create database `scms-pro` default character set utf8 default collate utf8_unicode_ci; # Add MySQL user mysql> create user 'scms'@'localhost' identified by 'mysql-pass'; mysql> grant all privileges on `scms-pro`.* to 'scms'@'localhost' with grant option; mysql> grant all privileges on `scms-pro`.* to 'scms'@'frontend';
Set Web Application parameters in /var/www/example.com/site/config.php:
// mysql define(_mysql_host, 'localhost'); define(_mysql_login, 'scms'); define(_mysql_pass, 'mysql-pass'); define(_mysql_db, 'scms-pro'); // auth define(_auth_service, 'ldap'); define(_ldap_host, 'ldap.ip.address'); define(_ldap_port, '389'); define(_ldap_base, 'ou=People,dc=cluster'); // hydra define(_hydra_hctl, '/etc/hydra/bin/hctl'); define(_hydrad_host, 'hydrad.ip');
Start web server:
service httpd restart
Verify installation by running http://example.com/install/verify.php. Everything except missing MySQL tables should be OK. General result should be Warning.
Populate MySQL database by running http://example.com/install/install.php
Delete install directory:
rm /var/www/example.com/install
Verify installation by running http://example.com/install/verify.php. General result should be OK.
Test connection to cluster http://example.com/ using your cluster account.
Troubleshooting
There are several sources of debugging information in SCMS.
Enabling "debug" option in site/config.php turns on debugging console in the bottom of web interface, showing all errors occurred during commands execution.
Setting "error_log" option to true in site/config.php enables writing errors to MySQL table error_log. It is useful during pre-production testing.
hydrad daemon reports some critical errors to syslog, see /var/log/messages.
FAQ
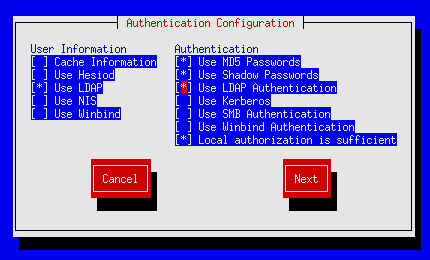
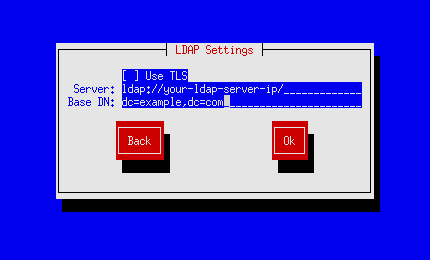
1. Configuring ldap authorization on server.
Scientific Linux SL release 5.7 or CentOS 5.7:
yum search authconfig yum install authconfig yum install nss_ldap authconfig-tui
2. Installing PAM authorization module for PHP in CentOS 5.x
yum install php-pear pecl search pam Retrieving data...0% MATCHED PACKAGES, CHANNEL PECL.PHP.NET: ======================================= PACKAGE STABLE/(LATEST) LOCAL PAM 1.0.3 (stable) 1.0.3 PAM integration pecl install PAM
Add to php.ini:
extension = "pam.so" pam.servicename = "php"
Set permissions to shadow file:
ls -l /etc/shadow -r-------- 1 root root 1858 Nov 6 17:20 /etc/shadow chgrp apache /etc/shadow chmod g+r /etc/shadow ls -l /etc/shadow -r--r----- 1 root apache 1858 Nov 6 17:20 /etc/shadow